Data
Computers can only perform arithmetic and logic operations in the
field
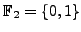 . A set of 8 bits is called a byte. The 8086 and 80286 had a 16-bit bus (the bus is the data
transfer capacity per clock tick); modern Intel-based processors have
32- or 64-bit wide buses. An
. A set of 8 bits is called a byte. The 8086 and 80286 had a 16-bit bus (the bus is the data
transfer capacity per clock tick); modern Intel-based processors have
32- or 64-bit wide buses. An 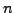 -bit wide memory chunk can hold
-bit wide memory chunk can hold 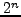 different values. These are either indexed from
different values. These are either indexed from 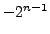 to
to
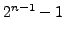 or from 0
to
or from 0
to 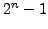 . An integer in C/C++ on an Intel
architecture is usually stored in 32 bits (=4 bytes). Floating point
values are stored (usually in 8 bytes) according to a specific
code. Any type of data that can be represented by an encoding of
finite-sized integers can be stored in a computer memory. In C/C++
data are categorized according to their types. Data types can be
elementary: bool (C++ only), char, short, int, long, float, double or user-defined:
union, struct, class (C++ only). A user-defined data
type is a finite sequence of existing data types and occupies either
the sum (struct, class) or the maximum (union) of
the sizes of the sequence elements. Memory addresses, by contrast,
normally occupy a fixed amount of storage (32 bits in 32-bit CPUs).
. An integer in C/C++ on an Intel
architecture is usually stored in 32 bits (=4 bytes). Floating point
values are stored (usually in 8 bytes) according to a specific
code. Any type of data that can be represented by an encoding of
finite-sized integers can be stored in a computer memory. In C/C++
data are categorized according to their types. Data types can be
elementary: bool (C++ only), char, short, int, long, float, double or user-defined:
union, struct, class (C++ only). A user-defined data
type is a finite sequence of existing data types and occupies either
the sum (struct, class) or the maximum (union) of
the sizes of the sequence elements. Memory addresses, by contrast,
normally occupy a fixed amount of storage (32 bits in 32-bit CPUs).
Leo Liberti
2008-01-12