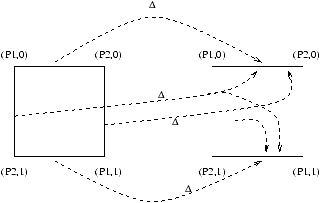
Figure 7: The binary consensus decision map from initial global states
to final global states
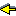


Figure 7: The binary consensus decision map from initial global states to final global states
Further work generalizes this simple geometric argument to the needed higher-dimensio-nal cases. In [Biran et al., 1988] a characterization of a class of problems solvable in asynchronous message-passing systems in the presence of a single failure was given. No generalization to more failures has since been solved using the same kinds of graph techniques. It was then a rather shared belief that one would have to use more powerful techniques in that case. The conjecture [Chaudhuri, 1990] that the k-set agreement problem (a kind of weak consensus; all is required is that the non-faulty processes eventually agree on a subset of at most k values taken from the input values) cannot be solved in certain asynchronous systems was finally proven in three different papers independently, [Borowsky and Gafni, 1993], [Saks and Zaharoglou, 1993] and [Herlihy and Shavit, 1993].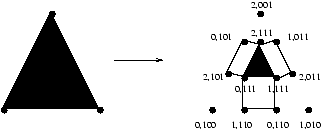
Figure 8: The synchronous protocol complex (for 3 processes) after one round


