Yann Ponty
Membre du LIX, Laboratoire d'Informatique de l'École Polytechnique
+33 1 77 57 80 95 · No Javascript = no email
- Prédiction du repliement, design et évolution de l'ARN
- Interactions ARN/ARN, ARN/Protéines, et Protéines/Protéines
- Génération aléatoire et combinatoire énumérative
- Algorithmique Discrète, Complexité paramétrée (Programmation dynamique !)
- Visualisation de l'ARN
NewsNominé comme référent HDR pour le dépt IDIA (Info&Interactions) d'IP Paris Prise de fonction comme directeur adjoint du LIX (X, IP Paris) pour la période 2025-2030 Honoré de ma nomination au "Board of Directors" de l'ISCB |
Recherche

Sur un plan scientifique, mes principaux centres d'intérêts se situent à l'interface entre Informatique, Mathématiques et Biologie Moléculaire. La finalité de mes travaux est principalement la conception d'approches analytiques, d'algorithmes efficaces et d'outils finalisés en direction de la biologie des Acides RiboNucléiques (ARN).
Quelques unes des questions soulevées sont les suivantes :
- Comment prédire la structure de l'ARN en présence de pseudonoeuds ?
- Quelle est la prévalence des phénomènes cinétiques à l'oeuvre au cours du repliement de l'ARN ?
- Quelle relation entre la structure et l'évolution des ARN ?
En quoi l'évolution des séquences d'ARN nous renseigne-t-elle sur leur structure ? - En quoi la connaissance de la structure d'un ARN est susceptible d'aider à l'analyse des données expérimentales ?
À l'inverse, comment tirer parti de données experimentales gros grain pour prédire la structure secondaire d'un ARN ? - Comment concevoir une séquence d'ARN réalisant une fonction souhaitée in vivo ?
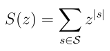
Certaines de ces questions ont trait à des propriétés universelles des biopolymères, et ne requièrent la prise en compte ni d'une séquence précise d'ARN, ni d'un modèle énergétique sophistiqué. En supposant qu'elles puissent être réexprimées à tel un niveau abstrait sans en sacrifier l'essence, j'utilise les outils issus de la combinatoire énumérative et de la combinatoire analytique pour obtenir des réponses quantitatives (asymptotiquement) exactes.
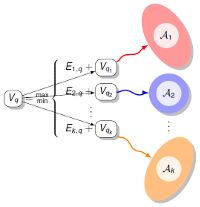
Des questions plus complexes exigent parfois une analyse spécifique de chaque séquence, tout en autorisant la mise en oeuvre d'algorithmes, souvent issus de la programmation dynamique, de complexité temps/mémoire polynomiales. Les concepts et principes sous-jacents à ces algorithmes sont alors parfois d'un niveau de généralité suffisant pour autoriser leur transposition à d'autres domaines. Par exemple, j'exporte en direction de la génomique comparative des méthodes ensemblistes introduites dans le contexte de la thermodynamique, entre autres afin de tester la robustesse des prédictions obtenues selon un principe de parcimonie.
Il arrive cependant que les problèmes considérés soient d'une difficulté algorithmique démontrable au sens de la théorie de la complexité. Dans ce cas, j'essaye d'établir l'origine de la difficulté du problème afin d'envisager des stratégies de contournement. Par exemple, on peut envisager la conception d'un algorithme de complexité paramétrée, ou encore une simplification du modèle sous-jacent au problème algorithmique, offrant un compromis acceptable entre expressivité and calculabilité en temps raisonnable.
Enfin, dans les cas extrêmes où le problème est difficile à appréhender, ou encore, de façon croissante, comme une approche préliminaire pour tester des hypothèses et me familiariser avec un problème, j'adopte une approche probabiliste, basée sur la génération aléatoire contrainte dans des distributions adéquates, telle la distribution uniforme, ou encore la distribution de Boltzmann.
Publications
| Par type | |
|---|---|
| Par thème | |
| Texte |
Cette liste est générée automatiquement à partir de HAL, et formattée via bibtex-js.
En cas de difficultés avec Javascript:
Visitez cette version statique
Logiciels
Bioinformatique des ARN
Design d'ARN
Analyse de séquences

GenRGenS
Bibliothèque pour la génération aléatoire de séquences génomiques structurées. Accepte plusieurs classes de modèles: grammaires pondérées, modèles de Markov (dont HMM), ProSITE patterns, expressions régulières ...
Collab.: A. Denise@Paris-Saclay Univ.
GenRGenS
Bioinformatique Structurale
Parcours
LIX · Ecole Polytechnique · France
LIX · Ecole Polytechnique · France
UMI PIMS/Maths Dept · Simon Fraser University · Canada
LIX · Ecole Polytechnique · France
IRIF · Université Paris Diderot · France
LIP6 · Sorbonne université · France
Biology Department · Boston College · USA
LRI · Université Paris-Saclay · France
School of Computer Science · Université Paris-Saclay · France
Administration, animation et service
Quelques unes de mes activités extra-scientifiques :- Responsable de l'équipe AMIBio@LIX · Depuis 2016
- Animateur (avec F. Cazals) du groupe de travail MASIM du Groupe de Recherche en Bioinformatique Moléculaire (GdR BIM) · Depuis 2014
- Membre élu (2016-2020) du conseil de laboratoire du LIX
- Membre du conseil scientifique pour les bases RNACentral et RFAM, maintenues à l'EMBL-EBI · Depuis 2019
- Membre du comité Gilles Kahn/SIF pour la meilleure thèse française en Informatique · Depuis 2018
- Membre du conseil scientifique du DIM RFSI · Depuis 2019
- Membre élu du comité national du CNRS en Informatique (Section 6) et Approches interdisciplinaires pour l'analyse du vivant (CID 51)
Activités éditoriales et relectures
- Éditeur associé pour la revue Bioinformatics, publiée par Oxford University Press · Depuis 2019
- Direction de comité de programme (ou track/area) pour
- Membre du comité de programme de
- RECOMB-CG'21
- SeqBIM'20
- ISMB'20
- RECOMB-CG'20
- APBC'20
- ISMB/ECCB'19
- ACM-BCB'19
- BICOB'19
- RECOMB'19
- APBC'19
- SeqBio'18
- GIW'18
- ISMB'18
- RECOMB'18
- BICOB'18
- ISMB/ECCB'17
- RECOMB'17
- BICOB'17
- SeqBio'16
- ECCB'16
- BioVis'16
- ISMB'16
- BICOB'16
- SeqBio'15
- WABI'15
- BioVis'15
- ISMB/ECCB'15
- BICOB'15
- ECCB'14
- BioVis'14
- ISMB'14
- BICOB'14
- ISMB/ECCB'13
- JOBIM'13
- BICOB'13
- BICOB'12
- JOBIM'12
- WRSBS'12
- JOBIM'11
- Relecteur régulier pour les revues
- PLOS computational biology
- Bioinformatics
- BMC Bioinformatics
- Journal of Mathematical Biology
- IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics
- Journal of Discrete Algorithms
- Algorithms for Molecular Biology
- PLOS One
- Journal of Theoretical Biology
- Theoretical Computer Science
- RNA
- Nucleic Acids Research
- Organisateur d'évènements scientifiques :
- Séminaire Dagstuhl : Rational Design of RiboNucleic Acids - 2022
- AlgoSB -- Mathematical and Computational Methods for Structured RNAs (Ecole thématique CNRS) - 2019
- RECOMB 2018 -- 22nd International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology - 2018
- CMSR'14 -- Colloque Computational Methods for Structural RNAs - 2014
- PARC -- Colloque PIMS Analytic RNA Combinatorics - 2014
- Journées ALEA (Ecole thématique CNRS) - 2011
- LIX bioinformatics colloquium - 2010
Enseignements
Bien que je consacre l'essentiel de mon activité à la recherche scientifique, j'interviens régulièrement au sein de cours de Master et, plus rarement, à un niveau licence.
Université Paris-Saclay · Palaiseau, France
- Cours 1 - Alignements [pdf]
- Cours 3 - Graphes et assemblage [pdf]
Enoncé TP - Chemins Euleriens et assemblage de k-mers [pdf] - Cours 2 - Structure de l'ARN [pdf]
Enoncé TP - Parsing, comptage et repliement de l'ARN [pdf] -
Liste des articles proposés pour présentation
- Alkan C, Karakoç E, Nadeau JH, Sahinalp SC and Zhang K (2006), "RNA–RNA Interaction Prediction and Antisense RNA Target Search", Journal of Computational Biology., mar 2006. Vol. 13(2), pp. 267-282. Mary Ann Liebert Inc. DOI
- Chikhi R, Limasset A, Jackman S, Simpson JT and Medvedev P (2015), "On the Representation of de Bruijn Graphs", Journal of Computational Biology., may 2015. Vol. 22(5), pp. 336-352. Mary Ann Liebert Inc. DOI
- Dondi R, Lafond M and Scornavacca C (2019), "Reconciling multiple genes trees via segmental duplications and losses", Algorithms for Molecular Biology., mar, 2019. Vol. 14(1) Springer Science and Business Media LLC. DOI
- Ferragina P and Manzini G (2005), "Indexing compressed text", Journal of the ACM., Jul 2005. Vol. 52(4), pp. 552-581. Association for Computing Machinery. DOI
- Hammer S, Wang W, Will S and Ponty Y (2019), "Fixed-parameter tractable sampling for RNA design with multiple target structures.", BMC bioinformatics., April 2019. Vol. 20, pp. 209. DOI
- Hoffmann S, Otto C, Kurtz S, Sharma CM, Khaitovich P, Vogel J, Stadler PF and Hackermifmmodeuelseüfiller J (2009), "Fast mapping of short sequences with mismatches, insertions and deletions using index structures", PLoS Computational Biology., Sep 2009. Vol. 5(9), pp. e1000502. DOI
- Limasset A, Cazaux B, Rivals E and Peterlongo P (2016), "Read mapping on de Bruijn graphs", BMC Bioinformatics., jun 2016. Vol. 17(1) Springer Science and Business Media LLC. DOI
- Medvedev P, Pham S, Chaisson M, Tesler G and Pevzner P (2011), "Paired de Bruijn Graphs: A Novel Approach for Incorporating Mate Pair Information into Genome Assemblers", Journal of Computational Biology., Nov 2011. Vol. 18(11), pp. 1625-1634. Journal of Computational Biology. DOI
- Miklos I, Meyer I and Nagy B (2005), "Moments of the Boltzmann distribution for RNA secondary structures", Bulletin of Mathematical Biology., sep 2005. Vol. 67(5), pp. 1031-1047. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. DOI
- Myers G (2013), "What's Behind Blast", In Models and Algorithms for Genome Evolution. , pp. 3-15. Springer London. DOI
- Reidys CM, Huang FWD, Andersen JE, Penner RC, Stadler PF and Nebel ME (2011), "Topology and prediction of RNA pseudoknots", Bioinformatics., feb 2011. Vol. 27(8), pp. 1076-1085. Oxford University Press (OUP). DOI
- Strothmann D (2007), "The affix array data structure and its applications to RNA secondary structure analysis", Theoretical Computer Science., dec 2007. Vol. 389(1-2), pp. 278-294. Elsevier BV. DOI
- Xu J and Berger B (2006), "Fast and Accurate Algorithms for Protein Side-Chain Packing", J. ACM. New York, NY, USA, jul 2006. Vol. 53(4), pp. 533–557. Association for Computing Machinery. DOI
Sorbonne Université · France
Fun stuffs* and ramblings
*Disclaimer: Acquired taste
Neil Gaiman's best tips for survival in an artistic academic career
Even though there are some difference between art and the academia, it is quite striking how some of Neil Gaiman's advise to young artists mirror what I would tell my students (with at least one notable exception... :) ).
The secret to keeping fruitful collaborations [skip to quote]
You get work however you get work, but people keep working [..] because their work is good, and because they're easy to get along with, and because they deliver the work on time. And you don't even need all three... two out of three is fine!
- People will tolerate how unpleasant you are if the work is good and you deliver it on time.
- People will forgive the lateness of your work if it's good and they like you.
- And you don't have to be as good as everyone else if you're on time and it's always a pleasure to hear from you.
Neil Gaiman, commencement speech at the University of the Arts Class of 2012
Of course, we should aim for the three out of three, but the observation of two being sufficient is spot on in my experience (and represents a parsimonious and flattering explanation to my continued academic employement despite my chronic tardiness :) ).
On impostor syndrom [skip to quote]
The first problem of [..] success is the unshakable conviction that you are getting away with something and that, any moment now, they will discover you.
[..] I was convinced there would be a knock on the door, and a man with a clipboard [..] would be there to tell me it was all over and they'd caught up with me and now I would have to go and get a real job, one that didn't consist of making things up and writing them down, and reading books I wanted to read...
And then I would go away quietly and get the kind of job where I would have to get up early in the morning and wear a tie and not make things up anymore.
Neil Gaiman, commencement speech at the University of the Arts Class of 2012
I guess most academics can relate to that (generally undeservedly), especially under the grind of our recurrent evaluations (institutions, employers, funding bodies, peers...). Although some of us already wear a tie to start with...
On emails [skip to quote]
There was a day when I looked up and realized that I had become someone who profesionnally replied to emails and who wrote as a hobby.
Neil Gaiman, commencement speech at the University of the Arts Class of 2012
An increasing number of my colleagues adopt quite extreme measures when it comes to email management (eg checking their emails only twice a day, or only within certain time slices...). I think it is one of the great challenge faced by humanity in the information era, and something we'll have to teach our children (academic), to find ways to limit the flow of information requiring active sprocessing (haven't found an acceptable solution myself... still looking).
On cheating on your CV (not an endorsement! :) ) [skip to quote]
People get hired because, somehow, they get hired... In my case I did something which these days would be easy to check and would get me into a lot of trouble and when I started out in those pre-internet days seemed like a sensible career strategy. When I was asked by editors who I'd written for, I lied. I listed a handful of magazines that sounded likely and I sounded confident and I got jobs. I then made it a point of honor to have written something for each of the magazines I've listed to get that first job, so that I hadn't actually lied, I'd just been chronologically challenged.
Neil Gaiman, commencement speech at the University of the Arts Class of 2012
This one I do not condone, of course, but working hard to deserve in retrospect whatever undeserved advantage you get at some point is a great attitude to adopt (cf impostor syndrom).
On luck [skip to quote]
Luck is useful. Often you'll discover that the harder you work, and the more wisely that you work, the luckier you will get but there is luck, and it helps.
Neil Gaiman, commencement speech at the University of the Arts Class of 2012
Parting words [skip to quote]
Be wise, because the world needs more wisdom, and if you cannot be wise pretend to be someone who is wise and then just behave like they would.
Neil Gaiman, commencement speech at the University of the Arts Class of 2012
If the shoe fits... (aka Python's duck typing :) ).
(Canadian) pennies for your thoughts
Background: In 2012, Canada decided to phase out the penny for its coinage system. Product prices may still use arbitrary cents (impractical otherwise since prices in Canada do not typically include taxes) but cash transactions are now rounded up/down to the closest multiple of 5 cents, as shown in the image below:

For instance, if two products A and B are worth 67¢ and 1\$21¢ respectively, one will have to pay 1\$80¢ to buy them together, instead of their accumulated price 1\$78¢. In this case, the seller makes an extra 2¢ in the transaction, thanks to the imperfect round-off. Mathematically speaking, it all depends on the remainder $r$ of the total price in a division by 5¢: If $r$ equals $1$ or $2$, than the seller looses $r$ cents, but if $r$ equals $3$ or $4$, then the seller makes an extra $5-r$ cents in the transaction.
With my wife, we were wondering: Can a supermarket manipulate the prices of its products in such a way that the rounded totals translate, on average, into an extra benefit for the company? We were not overly paranoid about it, but it seemed like a good opportunity to exercise our brain while strolling/bouldering (and, very occasionally, surfing) on the amazing beaches of Oahu's famed North shore...
As a first approximation, we can model the behavior of a shopper (oblivious to the imperfect change issue) as a Markov chain. In other words, given a list of products $A=\{a_i\}_{i=1}^k$, each associated with a price $p_i$, one chooses the $n$-th item $X_n$ with probability $${\mathbb P}(X_n=a\mid X_{n-1}\cdots X_{n-k})$$ which depends on his/her previous $k$ choices. On can then extend this Markov chain into remembering the remainder (modulo 5¢) $R_n$ of the total price after $n$ transactions. In this extended model, the probability of choosing a $n$-th item $X_n$ and ending with a remainder $R_n$, only depends on the previously chosen $k$-products, and the previous remainder $R_{n-1}$. With this in mind, the expected gain $G_n$ of the supermarket can now be written as $$ \mathbb{E}(G_n\mid A) = \sum_{a\in A}\left|\begin{array}{ll}+2\,{\mathbb P}((R_n,X_n)=(3,a)\mid R_{0}=0)\\+{\mathbb P}((R_n,X_n)=(4,a)\mid R_{0}=0)\\-{\mathbb P}((R_n,X_n)=(1,a)\mid R_{0}=0)\\-2\,{\mathbb P}((R_n,X_n)=(2,a)\mid R_{0}=0).\end{array}\right.$$ For small values of $n$, this expectation depends a lot on the list $A$ and its associated prices $p_i$. For instance if the customer buys a single item ($n=1$), the seller could set the remainder of all its prices to $3$ and make an easy additional 2¢ on each transaction.
However, for large values of $n$ (+assuming the ergodicity of the Markov chain), the stationary distribution can be assumed, i.e. the expected gain $\mathbb{E}(G_\infty\mid A)$ no longer depends on the initial state or, equivalently, on $n$. It is then possible to show that, no matter what the consummer preferences (i.e. the probabilities in the Markov chain), or the product list/prices $A$, one has $$\mathbb{E}(G_\infty\mid A)=0.$$ This can be proven thanks to a very elegant symmetry argument by James Martin on MathOverflow. In other words, there is simply no way for the supermarket to rig the game even if the consumer does not actively avoid being short-changed (but assuming that the consumer buys enough products, so the supermarket may and will still win in the end!).
What Feynman saw in a flower...
Because understanding the process does not necessarily make the result any less appealing! (otherwise, would there be any hope left for lasting companionship? ;) )
Beautiful work by Fraser Davidson.
If you haven't seen one of these...

... then you obviously never TA'ed Bioinformatics ;) (Lucky bastard!). Full credits/kudos to XKCD.
On another note (and yes, this will be my last xkcd strip, otherwise my page would simply end up being a mirror):

Best Journal ever!!!
Ever complained about the academic daily routine having become a quest for the best journal that would nevertheless accept one's half-cooked manuscript? Ever felt that citations and impact factors were way too overrated, and that selectivity should prevail? Look no further, as it is my pleasure to share my recent discovery of (arguably) the best journal ever!
With an acceptance rate way lower than 1%, the journal of universal rejection may rightfully pride itself of enforcing the strictest of academic standards (Nature beware!). Created in 2009, the journal solicits submissions in poetry, prose, visual art, and research. Despite such a wide scope, its widely competent editorial board can be trusted to lay an expert eye on your submission, and helpfully motivate its final decision.
P vs NP: The irrefutable proof ;)
Today is the day I almost died laughing while reading Scott Aaronson's Shtetl-Optimized blog dedicated to Complexity Theory. Ok, I know, this sort of humor alone may be regarded as a conclusive diagnostic by future generations of psychopathologists, but I'd still like to share his beautiful, human-centric, argument for why P != NP. Basically, he is asked the question:
He starts by stating the question in four informal ways, one of which is:
and adds
I woke up the following morning at the hospital, and must be clinically monitored during any future access to Scott's blog, but I encourage you to check it out for a daily dose of CS wittiness.
Amicable numbers
Amicable numbers are members of the number theory zoology (See their Wikipedia page), which, like trousers and all sorts of useful stuff, come handy in pairs. Formally, one starts by defining the restricted divisor function s(n) to be the sum of all divisors of n, itself excepted.
For instance for n = 220, one finds
Then, amicable numbers are pairs of natural numbers (p,q) such that s(p) = q and s(q) = p.
To make this notion explicit, we get back to the example above and find
and therefore (220,284) are amicable numbers.
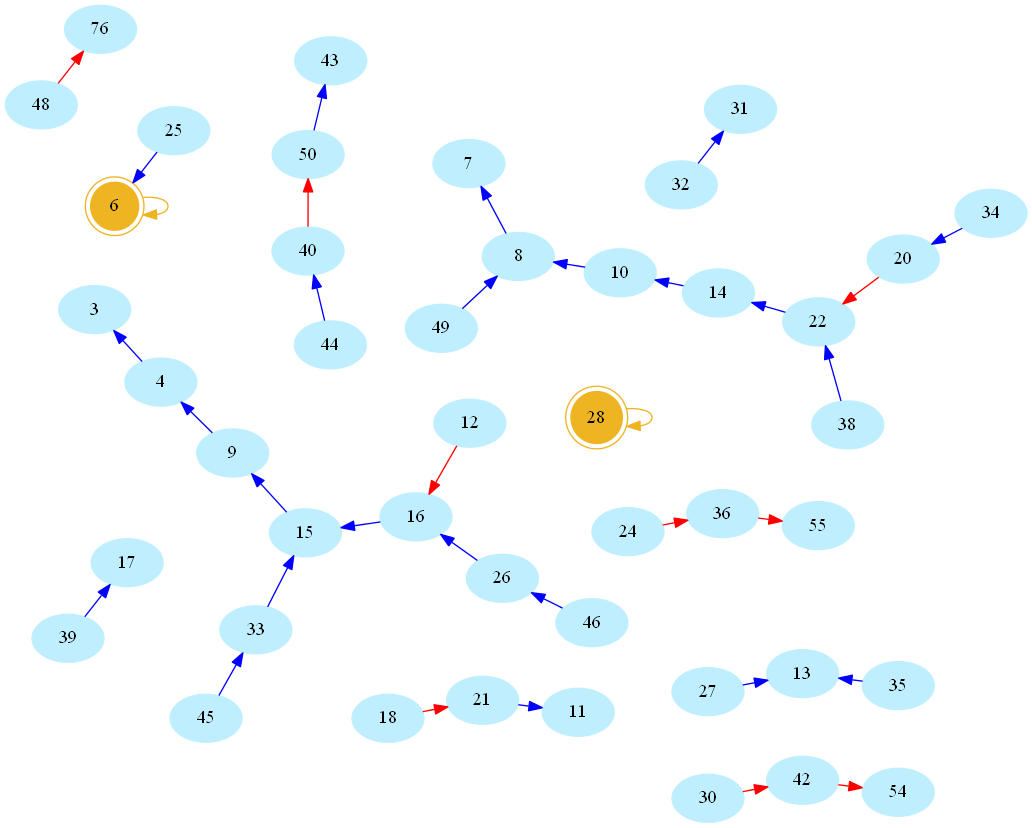
Now there is something about this definition that may sound arbitrarily limited to a computer scientist. Indeed, consider the (infinite) directed graph whose vertices are natural numbers, and whose edges are pairs (n,s(n)). Here is a picture, rendered using the allmighty GraphViz (neato mode), showing the resulting network/graph for numbers below 50 (blue/red arcs indicate decreasing/increasing values of s, number 1 omitted for readability, golden nodes are perfect numbers):
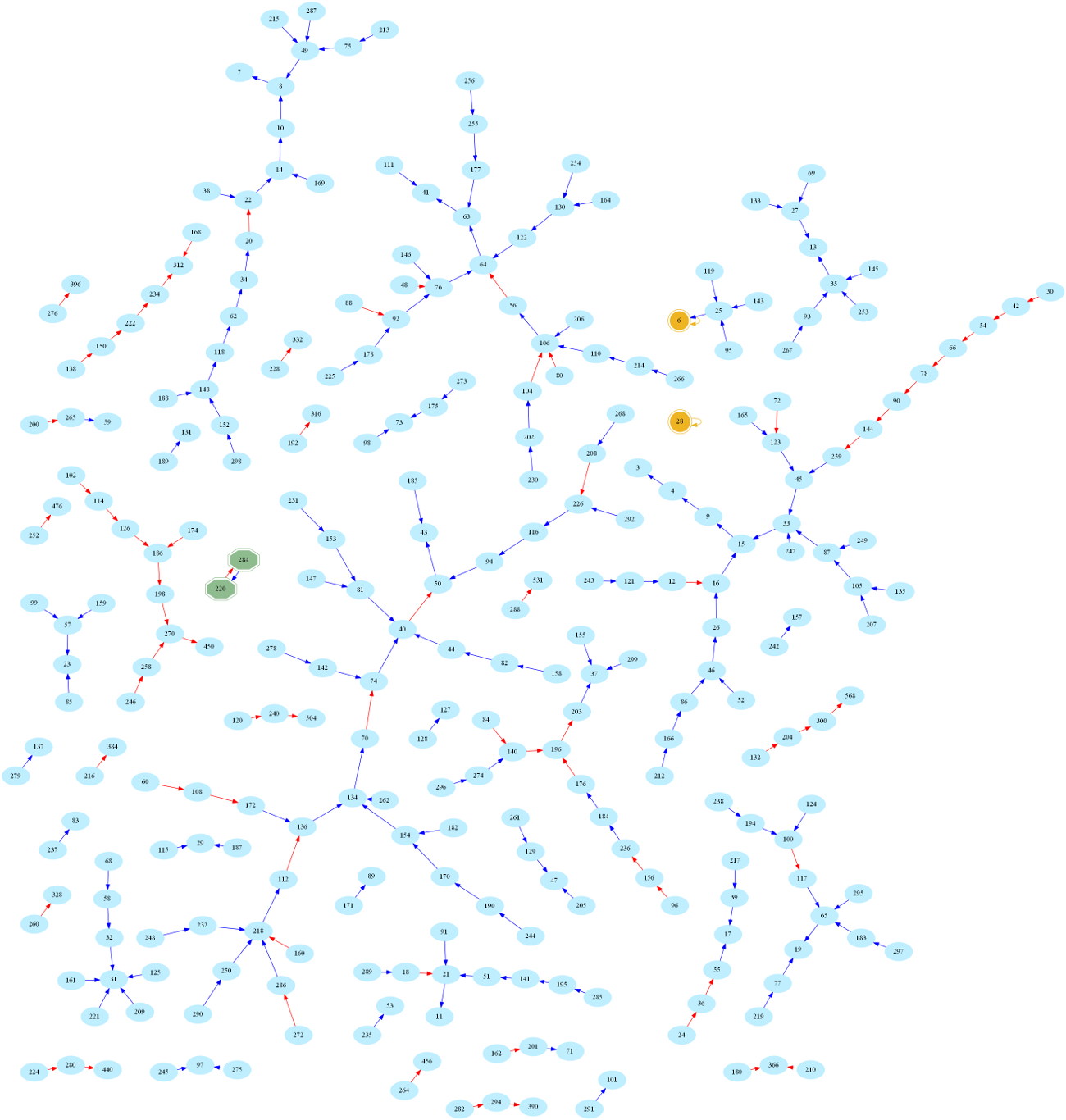
And here is the larger graph of numbers below 300 (Full-screen PDF version):
One then easily sees that amicable numbers are in bijection with cycles of length 2 in the graph. Indeed, zooming in on the above graph, one may easily spot the first amicable pair:
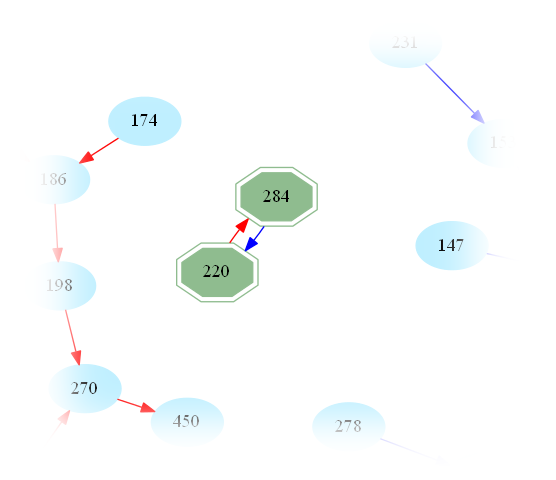
This raises the question
Indeed, one can alternatively, yet equivalently, define amicable numbers as pairs
which naturally generalizes into what is called sociable numbers, i.e. k-tuples of numbers
These sequences are also called periodic aliquot sequences. Here is one of the biggest periodic sequence known to date (k=28):
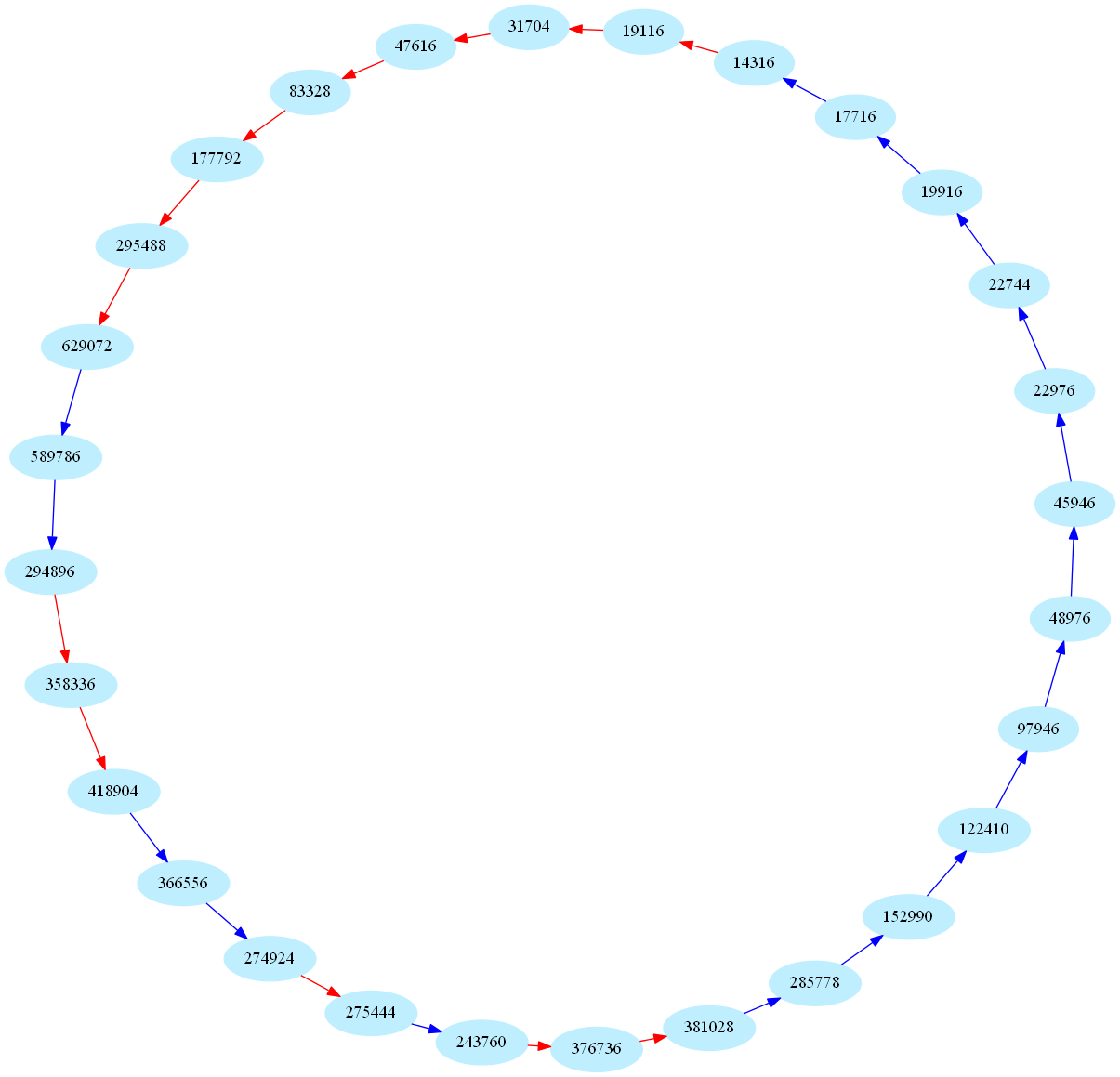
These numbers are currently of some interest in number theory:
For k=1, sociable numbers are perfect numbers.
For k=2, sociable numbers are amicable numbers.
In general, what are aliquot sequence of cycle length k? Do they even exist for large values of k?
Whether there exists a cycle-free infinite aliquot sequence is currently open!